Imaging Learning
Marie Curie International Reintegration Project No: 256581
Project Full Name: Linking hippocampus-dependent discriminative learning
to hippocampal neuronal ensemble separation using Arc/Homer1a FISH imaging.

Immediate-early genes (IEGs) are exploited as markers of neuronal activity because they are expressed immediately after structured neuronal activity. IEGs Arc and Homer1a have been used to visualize ensembles of hippocampal neurons active during two distinct behavioral epochs (Arc/Homer1a catFISH) and to revealed contextual specificity of the expression. CA1 and CA3 ensembles are more similar after repeated exploration of the same environment than after exploration of two different environments, resembling behavior of place cells in electrophysiological recordings.
This project examined the effects of behavioral experience on similarity between activated neuronal ensembles in the rat hippocampus and related cortical areas. It focused primarily on the separation (inverse similarity) between activated hippocampal ensembles as a potential mechanism of discriminative learning and cognitive coordination.
The primary goal of the project was establishing the Arc/Homer1a catFISH at the Institute of Physiology in Prague. This objective was fully achieved. A new laboratory of Molecular Imaging has been built and it is now routinely generating catFISH data. Furthermore, new imaging system has been acquired to allow acquisition of extensive image datasets. Since the limiting step of the technique is the time- and labor-consuming confocal image data analysis, a new software tool for automatic analysis of catFISH data has been developed in collaboration with Dr. Janáček, head of the Biomathematics department. This tool is currently tested and compared to the established semi-manual protocol and will provide material for methodic publication pending successful validation. (Figure 1).
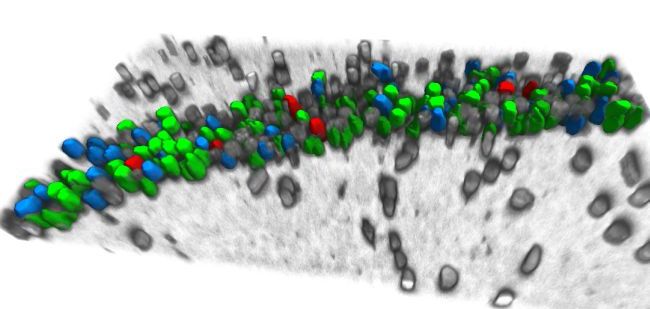
Figure 1.
Automatic segmentation of neuronal nuclei in a confocal image from a coronal section of area CA1 of rat hippocampus. Segmented nuclei are shown in color. Green – no signal; blue – single signal (Arc or Homer1a);
red – double signal (Arc+Homer1a)
Systemic administration of non-competitive NMDAR antagonists such as MK-801 (dizocilpine) is used to model schizophrenia in animals and people. MK-801 (0.15 mg/kg) impaired avoidance of a hidden place by rats foraging on a continuously rotating arena (Carousel), when misleading information from the irrelevant spatial frame was present, but not when it was absent. (Figure 2).
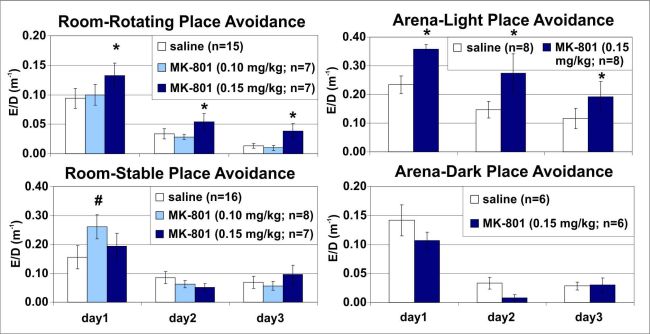
Figure 2.
Avoidance of a place hidden either in the reference frame of the room (left) or arena (right) was impaired by systemic MK-801 (0.15 mg/kg) when misleading information from the irrelevant spatial frame was present (top), but not when it was absent (bottom). The avoidance is measured as the number of entrances normalized by locomotion. ED - number of entrances per unit distance; * - significant effect of treatment; # - significant effect of treatment X session interaction
This result suggests that MK-801 compromised the ability to maintain separate coherent spatial representations of room and arena stimuli dissociated by the arena rotation. Importantly, it also eliminated contextual specificity of IEG expression when CA1 ensembles expressing Arc and Homer1a in two different environments were as similar as after repeated exploration of the same environment, whereas ensemble similarity in different environments was markedly lower in saline controls. (Figure 3).
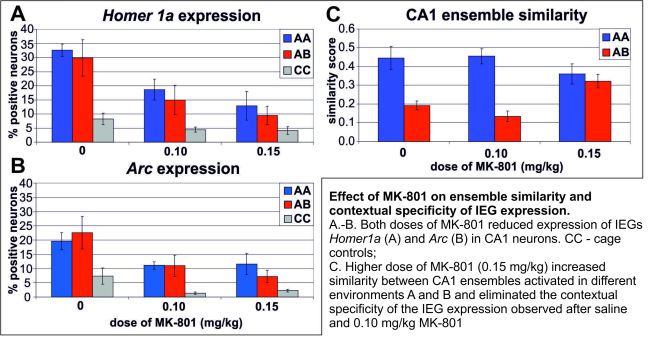
Figure 3.
Lower dose of MK-801 (0.10 mg/kg) showed no such effect on behavior or ensemble similarity, but both doses reduced overall IEG expression. (Figure 4).
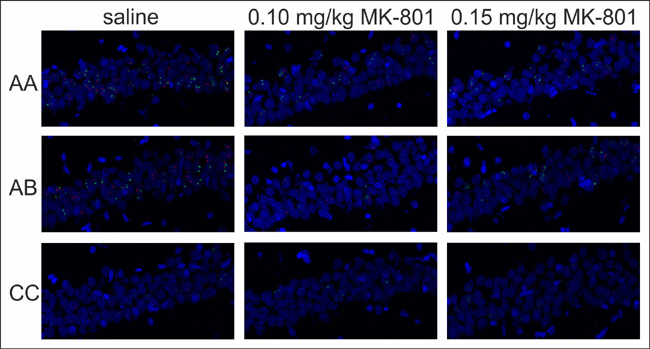
Figure 4.
IEG expression in CA1.
Representative images showing expression of Homer 1a (green) and Arc/Arg3.1 (red) triggered in the CA1 region of the hippocampus by exploration of the same (AA) or two different environments (AB) after an injection of saline or MK-801 (0.10 and 0.15 mg/kg). (CC)- caged controls.
These results suggest that a key aspect of schizophrenic cognitive symptomatology, compromised discrimination between relevant and irrelevant information, which likely contributes to the false sense of reality, can be due to deficit in cognitive coordination of discordant information into coherent subsets. They also demonstrate that this deficit may be straightforwardly modeled in experimental animals. This study has been published in Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience (Kubik et al., 2014; http://journal.frontiersin.org/Journal/10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00075/full).
Rats discriminating between two contexts two days after fear conditioning do not show greater separation between CA1 and CA3 ensembles than rats generalizing between the same contexts nine days after the conditioning. (Figures 5 and 6.)
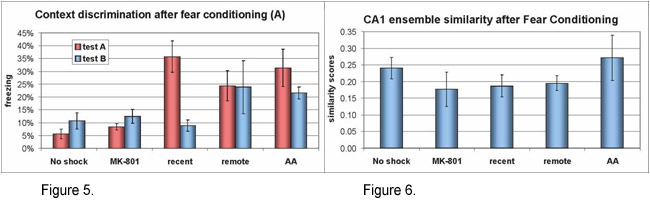
Figure 5.
Contextual Fear Discrimination. Contextual fear conditioning occurred in context A.
Rats tested for context discrimination 2 days later (Recent) showed markedly more freezing in the conditioning context A than in a modified context B.
In contrast, rats tested 9 days after the conditioning (Remote) showed equivalent amount of freezing in both contexts. Other rats received no shock during the conditioning or MK-801 injection (i.p.) 30 min before the conditioning. Some rats receive two test sessions in the conditioning context (AA).
Figure 6.
Similarity of CA1 ensembles activated by behavior depicted in Figure 5.
No significant differences were found between the groups.
Nevertheless, the ensemble similarity was rather low, indicating that separate ensembles may still facilitate context discrimination at the early, but not at the late time point. Lesions of the dentate gyrus (DG) markedly impaired place avoidance on the Carousel but largely spared spatial memory in the water maze supporting the notion that the DG facilitates separation of discordant information into coherent subsets. Interestingly, incremental training completely rescued the avoidance, indicating that "inescapable" stress in the aversively motivated task exacerbated the effect of the lesions. (Figures 7 and 8.)
Figure 7.
A rat entering a to-be avoided sector marked by an overhead blue light projection on to the arena surface during the Incremental place avoidance training protocol.
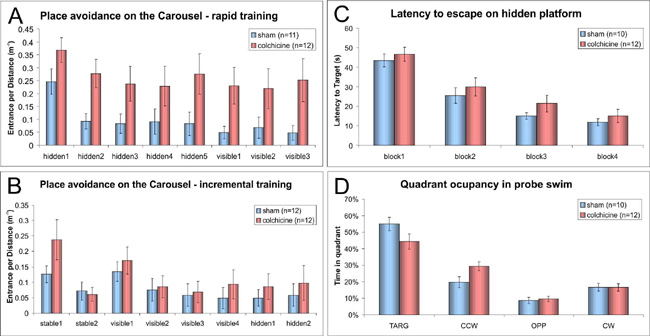
Figure 8.
Effect of lesions of the dentate gyrus.
A. The lesions markedly impaired place avoidance on a rotating arena (Carousel). hidden1-5 – avoidance of a place hidden in a reference frame of the room on a rotating arena; visible1-3 – avoidance of a place marked with a blue light projection; Navigation to a hidden goal in a water maze
B. and spatial memory for the location
C. were spared. block 1-4 – blocks of four trials; CCW – the counterclockwise quadrant; TARG – the target quadrant; OPP – the opposite quadrant; CW – the clockwise quadrant;
D. Incremental training protocol rescued the place avoidance. stable1-2 – avoidance of a marked place on a stationary arena.
These data will be prepared for publication pending ongoing stereological analysis of the extent of the lesion and potential collateral damage to other areas, evaluation of the stress response, and catFISH analysis of Arc/Homer1a expression.
Publications:
Kubik S, Buchtova H, Vales K, Stuchlik A (2014)
MK-801 impairs cognitive coordination on a rotating arena (Carousel) and contextual specificity of hippocampal immediate-early gene expression in a rat model of psychosis.
Front Behav Neurosci 8: 75.
Conferences:
Posters:
IBRO 2011, Florence, Italy; title: Specific deficit in cognitive coordination after systemic injection of dizocilpine (MK-801): Support for phenomenological validity of a pharmacological animal model of cognitive symptoms in schizophrenia
FENS 2012, Barcelona, Spain; title: Systemic MK-801 disrupts fear conditioning in a contextual discrimination task
SfN 2012, New Orleans, USA; title: Colchicine lesions of the dentate gyrus in rats severely disrupt rapid segregation of dissociated spatial information on a rotating arena (Carousel)
Physiological Days 2013, Prague, Czech Republic; title: Deficit in segregation of information from dissociated spatial frames on a rotating arena (Carousel) after systemic administration of MK-801 in an animal model of schizophrenia
FENS Featured Regional Meeting 2013, Prague, Czech Republic; title: Deficit in Ignoring Irrelevant Information (III) in an animal model of schizophrenia SfN 2013, San Diego, USA; title: Contextual fear discrimination, hippocampal ensemble separation and colchicine lesions of the dentate gyrus
Talks:
Behaviour 2013, Newcastle, UK; title: Immediate-early gene mapping of neural activity in spatial learning – talk presented by the fellow
Mikroskopie 2013, Lednice, Czech Republic; title: Segmentation of 3D confocal images of DAPI stained nuclei in hippocampus - presented by Dr. Janáček (collaborator)
EBPS 2013, La Rochelle, France; title: Coordination of discordant information on a rotating arena (Carousel) critically depends on the Dentate Gyrus - presented by Helena Buchtová (student)
Czech-Slovak Psychopharmacological Conference 2014, Jeseník, Czech Republic; title: Cognitive coordination on a rotating arena (Carousel): The problem of separation of conflicting information
Lectures:
Blending memories in the hippocampus: behavioral and neural hyperassociation in a pharmacological model of schizophrenia
Lecture given in May 2014 at the Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Warsaw, Poland within a bilateral cooperation project jointly funded by the Czech and Polish Academies of Sciences.




